Understanding ECG Readings for Beginners: A Step-by-Step Guide
The electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a vital diagnostic tool that records the heart’s electrical activity. Understanding how to read an ECG can seem daunting for beginners, but with a systematic approach, you can grasp the basics and become confident in interpreting its results. This blog will provide you with an easy-to-follow guide on understanding ECG readings.
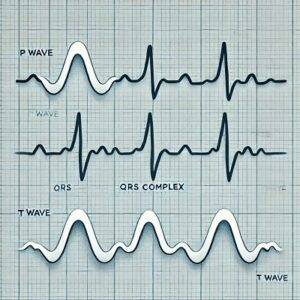
What is an ECG?
An ECG measures the electrical impulses generated by the heart as it contracts and relaxes, displaying these impulses as waveforms on paper or a digital screen. These waveforms provide crucial insights into heart rate, rhythm, and other factors that can indicate cardiac health or disease.
Basic Components of an ECG Reading
Before diving into interpretation, it’s important to understand the basic components of an ECG:
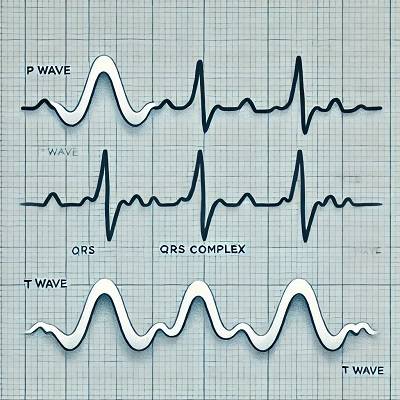
- P Wave: Represents atrial depolarization, meaning the electrical activity as the atria (upper chambers of the heart) contract.
- QRS Complex: Represents ventricular depolarization, or the contraction of the ventricles (lower chambers).
- T Wave: Represents ventricular repolarization, when the ventricles reset electrically after contracting.
- PR Interval: The time between the onset of the P wave and the start of the QRS complex, representing the delay as the electrical impulse travels from the atria to the ventricles.
- ST Segment: The flat section between the end of the S wave and the start of the T wave, representing the interval between ventricular contraction and repolarization.
- QT Interval: Measures the time from the start of the Q wave to the end of the T wave and reflects the total time of ventricular activity.
Step 1: Check the Heart Rate
One of the first things you’ll want to do when reading an ECG is to determine the heart rate. On an ECG, heart rate is typically measured in beats per minute (bpm). Here’s how to calculate it:
- Count the large squares between two consecutive R waves (the peak of the QRS complex). Divide 300 by the number of large squares between R waves to get the heart rate.
- For example, if there are four large squares between R waves, the heart rate is 75 bpm (300 ÷ 4 = 75).
Normal heart rate is between 60 and 100 bpm. Anything below 60 bpm is called bradycardia, and above 100 bpm is termed tachycardia.
Step 2: Evaluate Heart Rhythm
Heart rhythm refers to the regularity of heartbeats. To determine if the rhythm is regular:
- Check the consistency of the intervals between R waves (in the QRS complex).
- If the intervals are equal, the rhythm is regular. If they vary, it’s irregular.
A regular rhythm can be further classified as sinus rhythm if it originates from the sinus node (normal pacemaker of the heart). An irregular rhythm may indicate conditions like atrial fibrillation (AFib).
Step 3: Assess the P Waves
Look at the P waves:
- Are they present before every QRS complex?
- Are they uniform in shape and size?
A missing or abnormal P wave might indicate an arrhythmia, such as atrial fibrillation or flutter, where the atria are not contracting properly.
Step 4: Analyze the PR Interval
The PR interval is the time the electrical impulse takes to travel from the atria to the ventricles. A normal PR interval is between 0.12 and 0.20 seconds (3-5 small squares on the ECG graph).
A prolonged PR interval (> 0.20 seconds) may suggest first-degree heart block, where there is a delay in the conduction between the atria and ventricles. A short PR interval could indicate abnormal electrical pathways like in Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome.
Step 5: Examine the QRS Complex
The QRS complex represents ventricular depolarization. A normal QRS duration is less than 0.12 seconds (3 small squares).
- A widened QRS complex (> 0.12 seconds) suggests a bundle branch block, indicating a delay in the electrical impulse traveling through the ventricles.
- If the QRS is narrow and normal, it suggests the ventricles are functioning properly.
Step 6: Look at the ST Segment and T Wave
The ST segment should be flat (isoelectric). Any elevation or depression could indicate myocardial ischemia (insufficient blood flow to the heart), injury, or infarction (heart attack).
- ST elevation: A hallmark sign of a myocardial infarction (heart attack).
- ST depression: Could suggest ischemia or conditions like hypokalemia (low potassium).
The T wave should be upright in most leads. An inverted T wave may suggest ischemia, while a tall, peaked T wave might indicate hyperkalemia (high potassium).
Step 7: Measure the QT Interval
The QT interval reflects the total time for ventricular depolarization and repolarization. A prolonged QT interval can increase the risk of ventricular arrhythmias like torsades de pointes, a potentially dangerous condition.
Common Abnormal ECG Patterns
- Sinus Bradycardia: Heart rate less than 60 bpm with normal P, QRS, and T waves.
- Sinus Tachycardia: Heart rate greater than 100 bpm with normal P, QRS, and T waves.
- Atrial Fibrillation: Irregular rhythm, absence of P waves, and erratic baseline.
- Ventricular Tachycardia: A fast heart rate with a wide QRS complex.
- Myocardial Infarction: ST elevation in leads corresponding to the area of the heart affected.
Final Thoughts
Understanding ECG readings is an essential skill, particularly in the medical field. By following this step-by-step guide, beginners can gain confidence in interpreting ECGs. Start by checking the heart rate and rhythm, then move on to the P wave, PR interval, QRS complex, and finally the ST segment and QT interval. With practice, you’ll become adept at identifying normal and abnormal ECG patterns.




What Do Abnormal ECG Results Mean? A Comprehensive Guide - My Blog
[…] Read this………. […]