Understanding the Different Types of Oxygen Cylinders: Which is Best for Your Hospital?
Oxygen is essential in nearly every aspect of hospital care, from operating rooms to intensive care units (ICUs) and general wards. Hospitals rely on a consistent supply of medical-grade oxygen, often stored and delivered via cylinders. Understanding the various types of oxygen cylinders used in hospitals is crucial for maintaining efficient operations, ensuring patient safety, and meeting hospital-specific oxygen demands.
This blog will break down the different types of oxygen cylinder commonly used in hospitals and provide insights into which might be best suited for your healthcare facility.

1. Compressed Oxygen Cylinders
Overview:
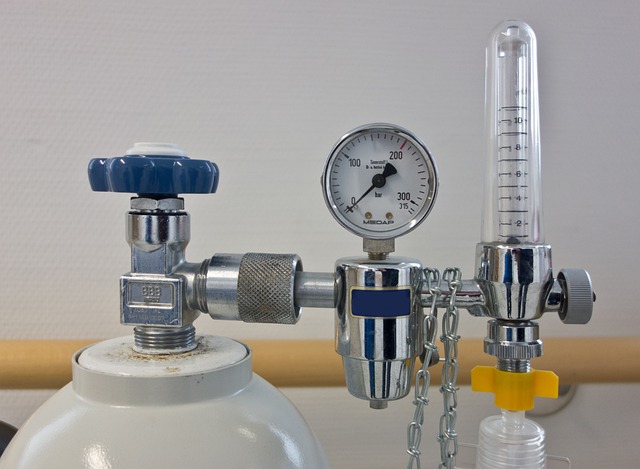
Compressed oxygen cylinders are the most commonly used type of oxygen storage in hospitals. These cylinders store oxygen in its gaseous form at high pressure (around 2,200 psi). The oxygen is released and regulated through a pressure regulator to deliver it at a flow rate appropriate for medical use.
Key Features:
- Sizes: Compressed oxygen cylinders come in various sizes, typically ranging from small portable cylinders (e.g., D and E cylinders) to larger units (e.g., H and M cylinders) that provide higher volumes of oxygen.
- Portability: Smaller cylinders are portable, allowing easy transportation for patient mobility or emergency use, while larger cylinders are typically stationary and used in fixed locations like ICU or operating rooms.
- Maintenance: These cylinders need regular refilling and require proper handling and storage to avoid leaks or damage.
Best For:
- Short-term or emergency oxygen supply.
- Smaller hospitals or specific departments needing portable oxygen.
2. Liquid Oxygen Cylinders
Overview:
Liquid oxygen cylinder store oxygen in its liquid state, which takes up significantly less space than its gaseous form. Liquid oxygen is stored at very low temperatures (-183°C), and when required, it is converted into gas for patient use. Hospitals use this type of cylinder when large volumes of oxygen are needed.
Key Features:
- High Storage Capacity: One of the major advantages of liquid oxygen cylinder is their ability to store large volumes in a compact form, making them ideal for hospitals with high oxygen demand.
- Lower Refill Frequency: Since liquid oxygen can store more in less space, hospitals can go longer without requiring refills compared to compressed oxygen cylinder.
- Special Storage Needs: Liquid oxygen needs to be stored in specially insulated tanks to maintain its low temperature and prevent evaporation losses.
Best For:
- Large hospitals or facilities with high oxygen consumption.
- Situations where continuous oxygen supply is critical.
3. Portable Oxygen Cylinders
Overview:
Portable oxygen cylinders are smaller, lightweight cylinders designed for patient mobility. These cylinders are typically filled with compressed oxygen and are easy to transport, making them useful in various settings within the hospital.
Key Features:
- Mobility: Portable oxygen cylinder is ideal for patients who need to move between wards or departments while still requiring oxygen therapy.
- Emergency Use: Often kept on standby in emergency rooms or ambulances to provide immediate oxygen support during patient transfers.
Best For:
- Emergency departments, transport, or temporary oxygen needs.
- Hospitals where mobility and portability are critical for patient care.
4. PSA Oxygen Generators and On-Site Cylinders
Overview:
Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA) oxygen generators allow hospitals to generate oxygen on-site from the ambient air. While not technically a “cylinder” system, PSA oxygen generation plants can provide hospitals with a steady, reliable supply of oxygen without relying on external deliveries. The oxygen can then be stored in cylinders for use.
Key Features:
- Continuous Oxygen Supply: PSA systems produce oxygen continuously, reducing reliance on external suppliers and ensuring uninterrupted availability.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Over time, generating oxygen on-site can be more cost-effective compared to purchasing and refilling external oxygen cylinders.
- Backup Oxygen: Cylinders connected to PSA plants can act as backup storage in case of a power failure or equipment malfunction.
Best For:
- Large hospitals with a high and consistent demand for oxygen.
- Hospitals looking to reduce operational costs and ensure supply-chain independence.
5. High-Pressure Oxygen Cylinder
Overview:
High-pressure oxygen cylinders store oxygen at pressures higher than standard compressed cylinders (often over 3,000 psi). These are designed for use in critical care or specialized applications where high flow rates of oxygen are required.
Key Features:
- Specialized Use: High-pressure oxygen cylinder is used in certain critical care situations, such as in hyperbaric oxygen therapy.
- Safety Considerations: Due to the higher pressure, these cylinders require specialized handling, storage, and safety precautions to prevent accidents.
Best For:
- Hospitals with hyperbaric oxygen therapy centers or departments that require higher oxygen flow rates for specific treatments.
6. Oxygen Concentrators (Alternative to Cylinders)
Overview:
Oxygen concentrators extract oxygen from the ambient air and deliver it directly to patients. Though not a cylinder, oxygen concentrators serve as a direct oxygen source in many hospitals, particularly in outpatient or long-term care settings.
Key Features:
- No Refilling Required: Oxygen concentrators eliminate the need for refilling cylinders, making them a practical solution for outpatient facilities.
- Limited Flow Rates: While convenient, oxygen concentrators are typically limited in the amount of oxygen they can deliver, making them unsuitable for high-demand settings.
Best For:
- Low-demand oxygen therapy in outpatient or home-care settings.
Conclusion: Which is Best for Your Hospital?
The best oxygen cylinder type for your hospital depends on your facility’s size, patient load, and specific oxygen demands. Large hospitals with high oxygen needs may benefit from the cost-efficiency of liquid oxygen or PSA systems, while smaller hospitals or departments requiring portability might prefer compressed or portable oxygen cylinder.







Leave a Reply