What Do Abnormal ECG Results Mean? A Comprehensive Guide
An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a common diagnostic tool used to evaluate the heart’s electrical activity. It can reveal crucial information about the heart’s rhythm, structure, and function. But what happens when you receive abnormal ECG results? Understanding what these results mean can be critical for early detection and treatment of heart conditions.
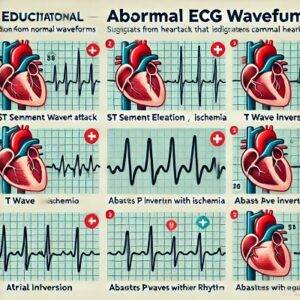
What is Considered an Abnormal ECG?
An abnormal ECG means that the electrical signals in your heart deviate from the standard patterns expected in a healthy heart. These deviations could indicate a wide range of conditions, from benign variations to life-threatening heart problems. Importantly, an abnormal ECG doesn’t always signal a severe issue, but it does warrant further investigation.
Common Causes of Abnormal ECG Results
Here are some common conditions that an abnormal ECG might suggest:
1. Arrhythmias (Irregular Heartbeats)
One of the most common causes of abnormal ECG readings is arrhythmias. Arrhythmias occur when the electrical impulses that regulate the heartbeat are irregular, too fast, or too slow. These irregularities can be identified through variations in the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave on the ECG reading.
- Atrial Fibrillation (AFib): A condition where the atria (upper chambers) beat irregularly. The P waves are often absent, and the rhythm is irregular. AFib increases the risk of stroke and heart failure if left untreated.
- Bradycardia and Tachycardia: Bradycardia refers to a heart rate that’s too slow (<60 bpm), while tachycardia refers to a heart rate that’s too fast (>100 bpm). These conditions can be diagnosed by checking the heart rate and rhythm on the ECG.
2. Myocardial Ischemia or Infarction (Heart Attack)
An ECG can reveal signs of insufficient blood flow to the heart (ischemia) or permanent damage to the heart muscle from a heart attack (myocardial infarction). Key signs include:
- ST Segment Elevation: One of the hallmark indicators of a heart attack. ST elevation in specific leads suggests the presence of acute myocardial infarction.
- ST Segment Depression: Can suggest ischemia, especially if you experience symptoms like chest pain.
- T Wave Inversion: This can indicate ischemia or heart attack, especially if seen in multiple ECG leads.
3. Bundle Branch Blocks
A bundle branch block occurs when there’s a delay or obstruction along the electrical pathways that make the heart beat. This results in a wider-than-normal QRS complex (greater than 0.12 seconds). Bundle branch blocks can affect the heart’s ability to pump efficiently and may be a sign of underlying heart disease or damage to the heart muscle.
- Right Bundle Branch Block (RBBB): Seen as a widened QRS complex, particularly in leads V1 and V2, but often has a benign prognosis.
- Left Bundle Branch Block (LBBB): A more serious finding than RBBB, as it often indicates more severe underlying heart conditions like hypertensive heart disease.
4. Electrolyte Imbalances
An ECG can reveal abnormal levels of electrolytes, such as potassium, calcium, and magnesium, which are essential for proper heart function.
- Hyperkalemia (High Potassium): Tall, peaked T waves are a classic sign of elevated potassium levels. If left untreated, hyperkalemia can lead to life-threatening arrhythmias.
- Hypokalemia (Low Potassium): Can present as flat T waves or U waves, indicating a risk for arrhythmias.
- Hypercalcemia and Hypocalcemia: These conditions affect the QT interval, where hypercalcemia shortens the QT interval and hypocalcemia lengthens it, both of which can lead to dangerous arrhythmias.
5. Pericarditis (Inflammation of the Heart Lining)
Pericarditis, an inflammation of the membrane surrounding the heart, can cause distinct changes on an ECG, including diffuse ST elevation (elevated in multiple leads) and PR segment depression. These changes are different from the localized ST elevation seen in myocardial infarctions.
Other Potential Causes of Abnormal ECGs
- Cardiomyopathy: Thickened or weakened heart muscle can alter ECG patterns, often resulting in changes in the size or shape of the QRS complex.
- Hypertrophy: Enlargement of the heart chambers can also show up as abnormal ECG readings, often as increased voltage in the QRS complexes.
- Congenital Heart Defects: Some structural abnormalities present from birth can lead to irregular ECG findings.
- Medication Effects: Certain medications, particularly those affecting heart rate or electrolyte balance (like beta-blockers, digoxin, or diuretics), can result in abnormal ECG patterns.
Non-Cardiac Causes of Abnormal ECGs
An abnormal ECG isn’t always due to heart disease. Other factors can cause irregular readings, including:
- Anxiety or Stress: Emotional stress can trigger transient ECG changes, particularly rhythm irregularities.
- Electrolyte Imbalances: Dehydration or kidney problems affecting electrolyte levels can cause abnormal ECGs.
- Lung Disease: Conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) can lead to abnormal ECG readings, such as right atrial enlargement or signs of strain on the right side of the heart.
What Should You Do if You Have Abnormal ECG Results?
If your ECG results are abnormal, follow these steps:
- Consult a Healthcare Professional: A cardiologist or your primary care doctor can interpret the significance of your results based on your symptoms, medical history, and any additional tests (such as echocardiograms or blood tests).
- Lifestyle Modifications: If your abnormal ECG is related to conditions like hypertension or electrolyte imbalances, changes such as improved diet, increased physical activity, and managing stress may be recommended.
- Medication or Further Testing: In some cases, your doctor may prescribe medication or recommend additional testing, such as a stress test, Holter monitor, or even cardiac catheterization, to determine the exact cause.
Conclusion
Abnormal ECG results can indicate a wide variety of heart conditions, from minor arrhythmias to more serious issues like heart attacks or electrolyte imbalances. While an abnormal ECG can be concerning, it is not always a definitive sign of a life-threatening condition. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment based on your specific circumstances.




Beauty Fashion
The articles you write help me a lot and I like the topic