What is the Difference Between Cardiac Arrest and Heart Attack?
When it comes to heart-related emergencies, cardiac arrest and heart attack are terms that are often used interchangeably, but they refer to very different conditions. Understanding the distinction between these two can make all the difference in responding effectively to an emergency.
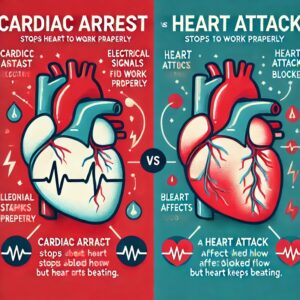
Difference Between Cardiac Arrest and Heart Attack
What is a Heart Attack?
A heart attack, also known as a myocardial infarction, occurs when blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked, typically due to a buildup of fat, cholesterol, and other substances that form a plaque in the coronary arteries. This blockage prevents oxygen from reaching the heart muscle, causing damage. The heart continues to beat during a heart attack, but the affected portion of the heart is deprived of oxygen, which can result in permanent damage if not treated quickly.
Symptoms of a heart attack can include:
- Chest pain or discomfort, often described as a squeezing or pressure sensation
- Pain radiating to the arm, jaw, back, or neck
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or vomiting
- Cold sweats and dizziness
Heart attacks are circulatory issues and while they can lead to serious complications, including cardiac arrest, they do not necessarily stop the heart from beating immediately
What is Cardiac Arrest?
In contrast, cardiac arrest is an electrical problem. It happens when the heart’s electrical system malfunctions, causing an irregular heartbeat or arrhythmia. As a result, the heart suddenly stops pumping blood to the brain, lungs, and other vital organs. When this occurs, the person loses consciousness almost immediately and has no pulse. Cardiac arrest is a medical emergency that can result in death within minutes if not treated with CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) or an AED (Automated External Defibrillator)
Key signs of cardiac arrest include:
- Sudden collapse
- No pulse
- No breathing
- Loss of consciousness
Unlike a heart attack, where the heart is still functioning, during cardiac arrest, the heart stops completely, and the brain and body are deprived of oxygen
The Connection Between Heart Attack and Cardiac Arrest
While a heart attack and cardiac arrest are different conditions, they are often linked. A severe heart attack can disrupt the heart’s rhythm, triggering cardiac arrest. However, cardiac arrest can also happen without any warning signs or prior heart issues. It’s important to note that immediate action is critical in both cases.
- For a heart attack, the priority is to restore blood flow, often through medication, surgery, or stents.
- For cardiac arrest, the focus is on restarting the heart using CPR or an AED to reset the heart’s electrical rhythm
What to Do in an Emergency
Recognizing the signs of a heart attack or cardiac arrest can be life-saving:
- For a heart attack: Call on emergency number immediately. If available, chew an aspirin, and stay calm while waiting for emergency medical help.
- For cardiac arrest: Call on emergency number immediately, and use an AED if available. Every second counts to restart the heart and prevent brain damage.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between cardiac arrest and heart attack is essential in ensuring the right response during an emergency. While both are serious, they are treated differently. Cardiac arrest requires immediate resuscitation, while a heart attack needs urgent medical intervention to restore blood flow.









Leave a Reply