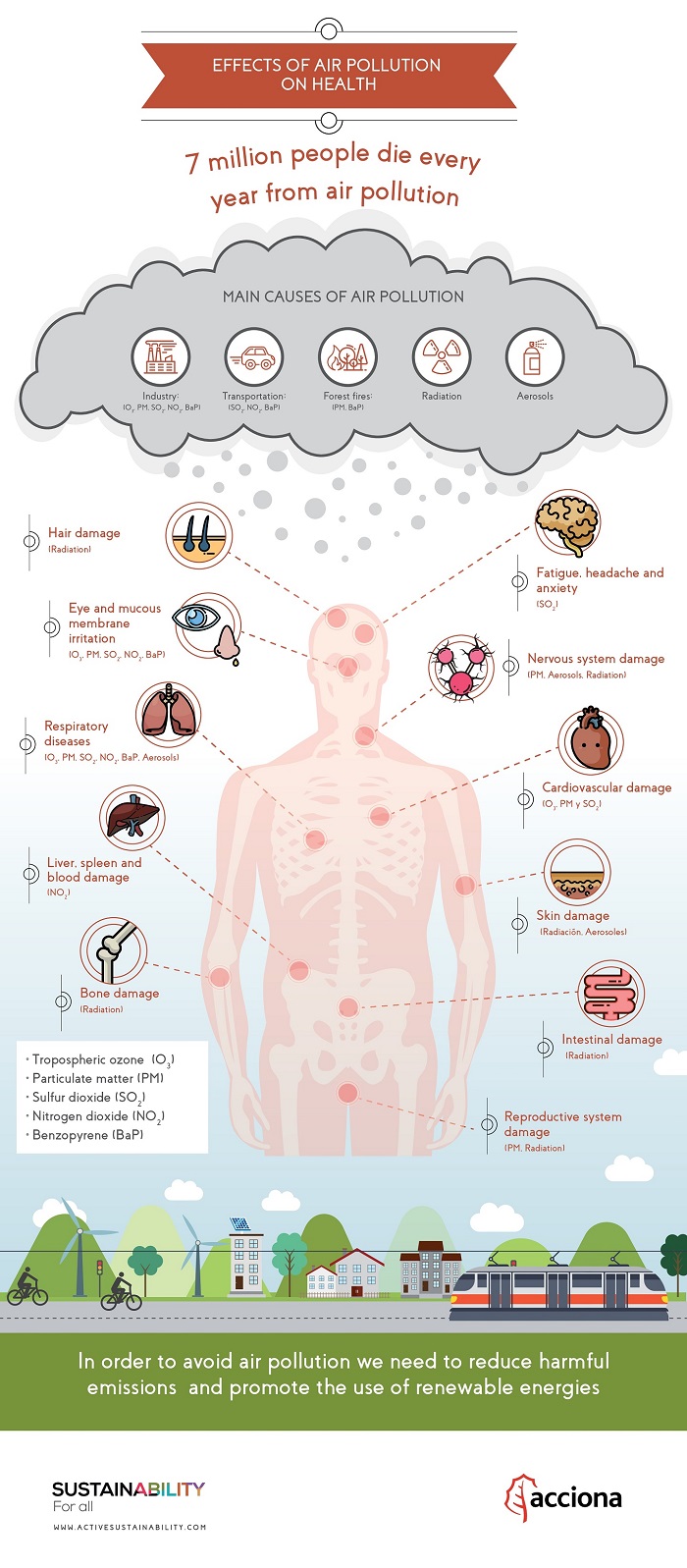
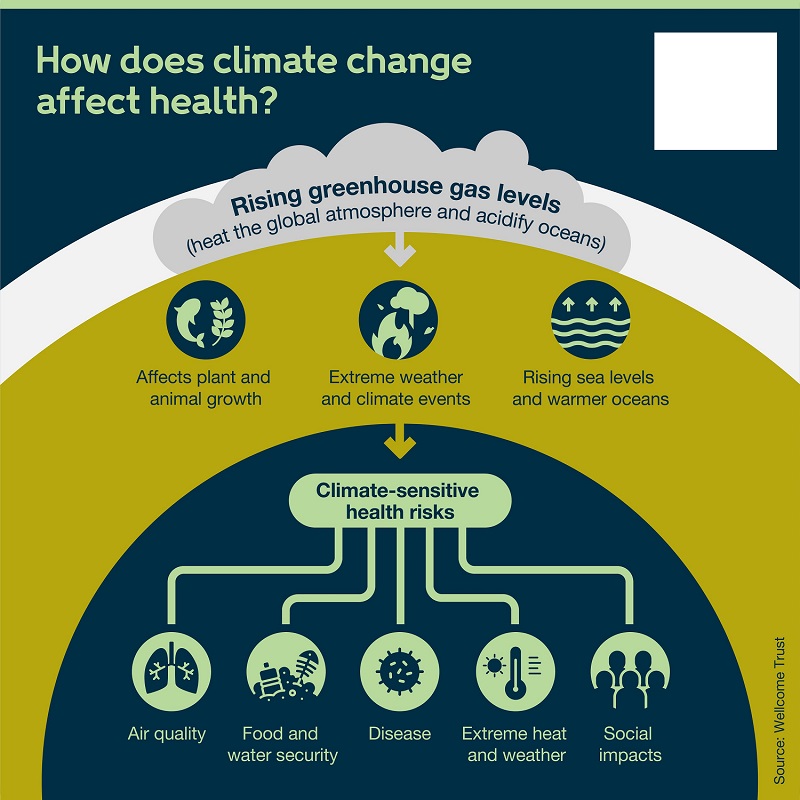
Air Pollution and Its Impact on Public Health
Air pollution is a silent yet pervasive threat to global health, affecting millions worldwide. Defined as the presence of harmful substances in the atmosphere, air pollution originates from various sources like industrial emissions, vehicular exhaust, natural events (such as wildfires), and household activities. The impact on public health is profound, ranging from minor respiratory discomfort to severe cardiovascular and neurological diseases.
Types of Air Pollutants
- Particulate Matter (PM)
- PM2.5 and PM10 are microscopic particles that can penetrate deep into the lungs and bloodstream, causing respiratory and cardiovascular issues.
- Nitrogen Dioxide (NO₂)
- A significant byproduct of burning fossil fuels, linked to asthma and reduced lung function.
- Ozone (O₃)
- Ground-level ozone contributes to respiratory problems, especially in children and the elderly.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO)
- High exposure interferes with oxygen delivery to organs and tissues.
- Sulfur Dioxide (SO₂)
- Known to cause irritation of the respiratory system and exacerbate asthma.
Health Impacts of Air Pollution
- Respiratory Issues
- Chronic exposure leads to conditions like asthma, bronchitis, and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). It also exacerbates symptoms in individuals with pre-existing lung conditions.
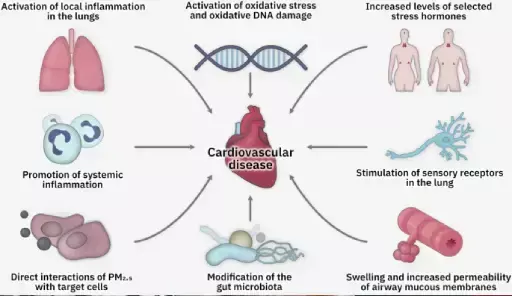
- Cardiovascular Diseases
- Fine particulate matter increases the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and hypertension by causing inflammation and oxidative stress.
- Cancer
- Prolonged exposure to carcinogenic pollutants, such as benzene and diesel exhaust, is linked to lung and bladder cancer.
- Neurological Effects
- Air pollution has been associated with cognitive decline and developmental issues in children, as well as an increased risk of dementia in older adults.
- Pregnancy and Infant Health
- Exposure during pregnancy can result in low birth weight, premature births, and developmental delays in children.
Global Public Health Burden
- The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that air pollution causes 7 million premature deaths annually.
- Regions with high industrialization and urbanization, like Asia and Africa, bear a disproportionate burden.
Strategies to Mitigate the Health Impact
- Policy Interventions
- Implementation of clean air regulations and standards for industrial emissions.
- Transitioning to renewable energy sources.
- Urban Planning
- Increasing green spaces to filter air pollutants.
- Promoting public transportation and cycling to reduce vehicular emissions.
- Technological Solutions
- Use of air purifiers and cleaner industrial technologies.
- Adoption of electric vehicles (EVs).
- Public Awareness
- Educating communities about the risks of air pollution and ways to minimize exposure, such as using masks and avoiding outdoor activities during high-pollution periods.
Call to Action
Air pollution is a global challenge that requires collective efforts. Governments, industries, and individuals must work together to mitigate its effects. Small changes, such as reducing energy consumption, planting trees, and advocating for stricter environmental laws, can contribute significantly to improving air quality and public health.
By addressing air pollution, we not only protect the environment but also enhance the quality of life for future generations.







Hairstyles
Thank you for the auspicious writeup. It in fact was a amusement account it. Look advanced to far added agreeable from you! By the way, how can we communicate?