Bridging the Gap: Strategies to Enhance Access to Quality Rural Healthcare Services
Access to quality healthcare is a global concern, especially in rural and under-served regions where geographical, financial, and logistical barriers hinder the delivery of essential medical services. Bridging this gap is essential to improving health outcomes and reducing disparities. This article outlines key strategies to enhance healthcare access in rural areas.
1. Strengthening Healthcare Infrastructure
One of the foremost challenges in rural healthcare is inadequate infrastructure. To address this:
- Expand Medical Facilities: Build primary health centers (PHCs) and community health clinics in remote areas.
- Mobile Clinics: Deploy mobile medical units equipped with essential diagnostic and treatment facilities to serve isolated communities.
- Telemedicine Hubs: Establish telemedicine centers to connect rural patients with specialists in urban hospitals.
2. Workforce Development
A shortage of trained healthcare providers is a persistent issue in rural areas. Solutions include:
- Training Local Workforce: Initiate programs to train community health workers and mid-level healthcare providers.
- Incentives for Rural Service: Offer financial incentives, scholarships, and career advancement opportunities to encourage healthcare professionals to work in rural settings.
- Task Shifting: Empower nurses and paramedics to perform specific medical tasks, relieving the workload on physicians.
3. Leveraging Technology
Innovative technologies can significantly enhance healthcare access:
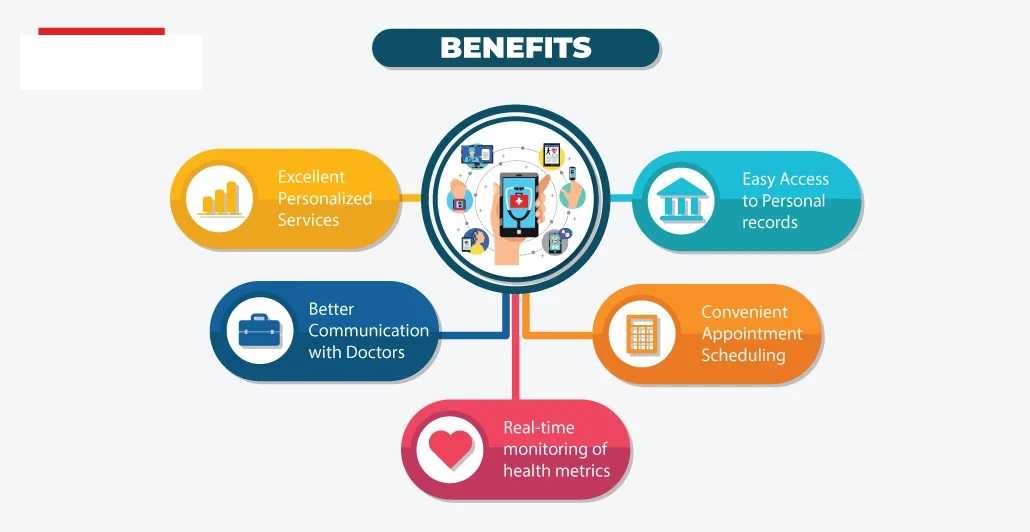
- Telemedicine: Provide remote consultations and follow-ups through video calls and apps, reducing the need for travel.
- Digital Health Records: Implement electronic health records (EHRs) to streamline patient management and improve continuity of care.
- AI and Diagnostics: Use artificial intelligence-powered diagnostic tools for faster and more accurate disease detection.
4. Enhancing Transportation and Accessibility
Transportation barriers often delay timely medical intervention:
- Emergency Transport Services: Establish ambulance networks equipped to handle emergencies in remote locations.
- Improved Roads: Advocate for better road networks to connect rural communities with healthcare facilities.
5. Addressing Financial Barriers
Healthcare affordability is a significant hurdle in rural areas:
- Subsidized Healthcare Services: Provide low-cost or free medical services to economically disadvantaged populations.
- Health Insurance Coverage: Expand government health insurance programs to cover rural populations comprehensively.
- Microfinance Initiatives: Support community financing schemes to enable families to access healthcare services.
6. Community Engagement and Awareness
Community involvement is critical for the success of rural healthcare programs:
- Health Education: Conduct awareness campaigns on preventive healthcare, nutrition, and hygiene.
- Community Participation: Engage local leaders and community members in planning and implementing healthcare initiatives.
- Behavioral Change Communication (BCC): Design programs to address cultural or societal barriers to seeking medical care.
7. Fostering Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs)
Collaborations between governments, NGOs, and private healthcare providers can amplify efforts:
- Co-Funding Projects: Share resources to establish and operate healthcare facilities.
- Outreach Programs: Partner with NGOs to run health camps and vaccination drives.
- Innovative Models: Implement PPPs for mobile health units, telemedicine services, and supply chain improvements.
8. Promoting Preventive Healthcare
Preventive measures can reduce the burden of diseases in rural areas:
- Screening Programs: Regular health check-ups for early detection of chronic conditions like diabetes and hypertension.
- Immunization Drives: Increase vaccination coverage to prevent infectious diseases.
- Sanitation and Hygiene Initiatives: Promote safe drinking water, sanitation, and hygiene practices.
9. Policy and Advocacy
Robust policies and political will are necessary for long-term change:
- Rural Health Missions: Implement national programs focused on rural healthcare, such as India’s National Health Mission (NHM).
- Resource Allocation: Advocate for increased funding and resources for rural healthcare development.
- Monitoring and Accountability: Set measurable goals and ensure transparency in the implementation of healthcare programs.
Conclusion
Enhancing healthcare access in rural areas requires a multi-faceted approach combining infrastructure development, workforce training, technological innovation, and community engagement. Governments, healthcare providers, and organizations must collaborate to create sustainable and inclusive healthcare solutions. Bridging the rural healthcare gap is not just a matter of health equity—it is a step toward creating resilient and healthier societies worldwide.







Leave a Reply