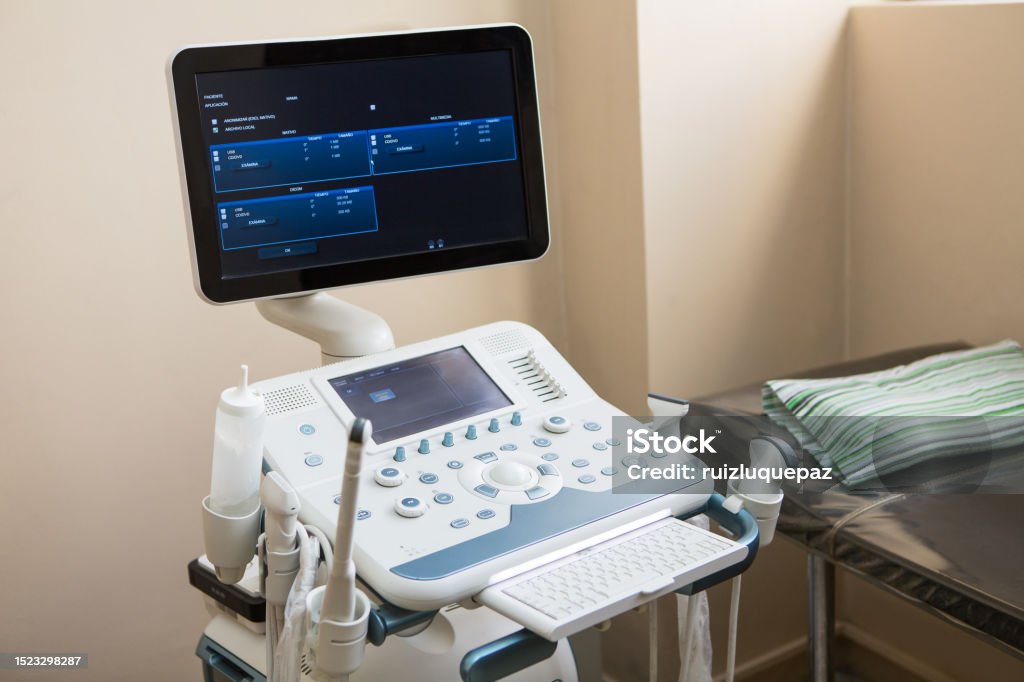
Understanding 2D Ultrasound with Color Doppler: Basics and Applications
2D ultrasound with color Doppler technology has become an essential tool in diagnostic imaging. It combines traditional grayscale ultrasound with Doppler imaging to provide a two-dimensional view of the body’s internal structures along with blood flow dynamics. This powerful combination enables healthcare professionals to gain a comprehensive understanding of organ function, detect abnormalities, and monitor various conditions effectively.
What is 2D Ultrasound?
2D ultrasound, also known as grayscale ultrasound, produces a flat, two-dimensional image by sending high-frequency sound waves through the body. These waves bounce off organs and tissues and are then captured by a transducer, creating a real-time visual of internal structures. The grayscale images help clinicians view organs, soft tissues, and other structures in detail, making it ideal for assessing anatomical features and guiding certain procedures.
What is Color Doppler?
Color Doppler ultrasound adds another layer of information by visualizing blood flow within the vessels. The Doppler effect captures the movement of red blood cells, enabling the machine to detect the speed and direction of blood flow and displaying it in different colors. Typically, red and blue indicate the direction of blood flow—toward or away from the transducer—allowing healthcare providers to assess circulation and identify blockages, clots, or other vascular issues. This capability is especially beneficial in evaluating blood vessels, the heart, and monitoring blood flow in certain organ systems.
How Does 2D Ultrasound with Color Doppler Work?
The combined technology of 2D imaging with Doppler features allows the machine to produce detailed anatomical images alongside functional data about blood flow. The transducer, placed on the skin’s surface, emits sound waves that penetrate the body, reflecting off structures and returning to the device. For Doppler imaging, the system calculates the frequency shifts that occur as the sound waves bounce off moving blood cells. The device translates these frequency shifts into color-coded images, which display on the monitor in real time.
Applications of 2D Ultrasound with Color Doppler
This combination is used across a variety of medical fields for numerous diagnostic applications:
- Cardiovascular Health
- Heart Health: Color Doppler ultrasound is frequently used in echocardiography to visualize heart chambers, valves, and blood flow patterns, providing insights into conditions like valve stenosis, regurgitation, or septal defects.
- Blood Vessel Analysis: It allows for real-time visualization of blood flow within vessels, helping to identify atherosclerosis, aneurysms, and peripheral artery disease.
- Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Fetal Monitoring: During pregnancy, Doppler ultrasound assesses blood flow in the umbilical cord, fetal heart, and maternal-fetal circulation. This helps to monitor fetal development and detect abnormalities.
- Ovarian and Uterine Health: It aids in evaluating ovarian cysts, uterine fibroids, and blood flow issues in reproductive organs.
- Vascular Studies
- Vein and Artery Analysis: Color Doppler is invaluable for diagnosing deep vein thrombosis (DVT), arterial blockages, and other vascular abnormalities. This is critical for conditions where impaired blood flow can lead to severe complications.
- Aneurysm Detection: The technology is also employed to detect abnormal dilation in blood vessels, such as an aneurysm, by visualizing irregular blood flow patterns.
- Liver and Kidney Evaluation
- Doppler ultrasound is used to assess the portal and renal veins. Abnormal blood flow in these organs can signal various conditions, such as portal hypertension in the liver or renal artery stenosis in the kidneys.
- Musculoskeletal Imaging
- It can visualize blood flow in muscles and joints and assess blood supply to different tissues. This is particularly useful for patients with musculoskeletal injuries or chronic conditions affecting blood flow.
Benefits of 2D Ultrasound with Color Doppler
- Non-invasive and Safe: 2D Doppler ultrasound is radiation-free and safe for repeated use, making it suitable for monitoring conditions over time.
- Real-time Visualization: This allows for dynamic assessments, especially valuable in evaluating cardiac function or observing fetal movement.
- Widespread Accessibility: It’s relatively affordable and widely available, offering a practical diagnostic option for many healthcare settings.
Limitations and Considerations
While 2D Doppler ultrasound is versatile and informative, it has limitations:
- Image Quality: The quality can depend on factors like patient body type and skill level of the operator.
- Depth Limitation: Deeper structures may not be as clear, and dense tissues or gas can hinder sound wave transmission.
- Interpretation of Blood Flow: For certain conditions, 3D imaging or other modalities like MRI may provide more comprehensive data.
Conclusion
The combination of 2D ultrasound with color Doppler has revolutionized diagnostic imaging by providing real-time visualization of both structural and functional information. It plays an essential role in the management of cardiovascular health, fetal monitoring, vascular studies, and more, offering healthcare providers a reliable, non-invasive tool for a wide range of medical assessments. Its accessibility, versatility, and safety make it an indispensable asset in modern diagnostics.






Hairstyles
Thanks for the a new challenge you have exposed in your text. One thing I want to comment on is that FSBO associations are built as time passes. By bringing out yourself to owners the first weekend their FSBO will be announced, before the masses commence calling on Wednesday, you build a good link. By sending them instruments, educational supplies, free reviews, and forms, you become a strong ally. By taking a personal desire for them as well as their situation, you develop a solid link that, many times, pays off in the event the owners decide to go with a broker they know and also trust — preferably you.