Understanding Medical Gas Pipeline Color Coding as per HTM-02 Guidelines: A Comprehensive Guide for Hospitals
Medical gas pipelines are the lifeline of any hospital, delivering critical gases like oxygen, nitrous oxide, medical air, and vacuum to patient care areas. To ensure safe and efficient delivery of these gases, it’s crucial to follow standardized guidelines. In the UK, the Health Technical Memorandum (HTM) 02-01 provides a detailed framework for medical gas pipeline systems (MGPS), including the essential color coding to prevent accidents and confusion.
This blog explores the key color coding guidelines outlined in HTM-02 and explains their significance for hospital staff, engineers, and facility managers.
What is HTM-02?
HTM-02-01 is a comprehensive technical document issued by the UK Department of Health. It covers the design, installation, operation, and maintenance of medical gas pipeline systems (MGPS) in healthcare facilities. The document ensures that gases are delivered safely, without cross-contamination, and in compliance with legal safety standards.
Importance of Medical Gas Pipeline Color Coding
The color coding of medical gas pipelines is crucial for several reasons:
- Safety: Incorrect gas administration can lead to severe medical errors, making clear and distinct color coding essential for patient safety.
- Efficiency: Quick identification of gases during emergencies or routine care helps healthcare providers administer treatment swiftly and accurately.
- Compliance: Adhering to HTM-02 standards ensures that hospitals meet the legal and safety requirements for healthcare environments.
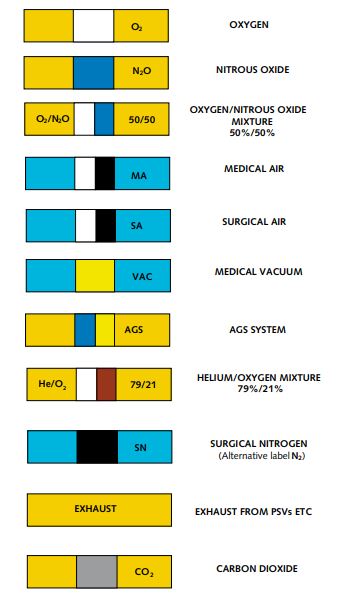
Medical Gases and Their Color Coding as per HTM-02
Here’s a breakdown of common medical gases and their respective color codes as specified in the HTM-02-01 guidelines:
1. Oxygen (O₂)
- Pipeline Color: White (RAL 9010)
- Cylinder Color: White shoulder
- Usage: Oxygen is one of the most crucial medical gases used for respiratory support and life-saving interventions.
2. Nitrous Oxide (N₂O)
- Pipeline Color: Blue (RAL 5010)
- Cylinder Color: Blue shoulder
- Usage: Used primarily in anesthesia and pain management.
3. Medical Air
- Pipeline Color: Black and white stripes
- Cylinder Color: Black and white stripes
- Usage: Supplies clean air to ventilators and other respiratory devices.
4. Vacuum (Suction)
- Pipeline Color: Yellow (RAL 1018)
- Usage: Removes bodily fluids, secretions, or air from patients during surgeries and critical care procedures.
5. Carbon Dioxide (CO₂)
- Pipeline Color: Grey (RAL 7037)
- Cylinder Color: Grey shoulder
- Usage: Primarily used in minimally invasive surgeries to inflate body cavities and for specialized medical procedures.
6. Entonox (50% Nitrous Oxide, 50% Oxygen Mix)
- Pipeline Color: Blue and white
- Cylinder Color: Blue and white
- Usage: Commonly used for pain relief during childbirth and minor surgical procedures.
Additional Requirements for HTM-02 Compliance
- Pipeline Identification: Beyond color coding, HTM-02-01 mandates that each pipeline be clearly labeled with the name of the gas and direction of flow at regular intervals (approximately every 3 meters).
- Alarm Systems: Hospitals must install alarm systems to monitor medical gas supplies and provide immediate alerts in case of leaks or pressure drops.
- Maintenance Protocol: Routine checks and maintenance are essential to ensure that pipelines are free from leaks and are operating safely.
Ensuring Proper Training for Healthcare Providers
Even with robust color coding, the risk of human error remains. Hospitals should implement mandatory training programs for all staff involved in the use and management of medical gases. This includes:
- Recognizing gas types based on pipeline color codes and labels.
- Properly handling and administering medical gases.
- Understanding safety protocols, including emergency shutdown procedures and alarm response.
Training ensures that hospital staff can respond quickly and correctly, minimizing the risk of accidents.
Regular Audits and Inspections
In addition to training, it’s important to perform regular audits and inspections of the MGPS to ensure ongoing compliance with HTM-02. These audits should focus on:
- Verifying that all pipelines are correctly labeled and color-coded.
- Ensuring alarm systems are functional and responding accurately.
- Checking the overall condition of the gas delivery system for any signs of wear, tear, or damage.
Conclusion
In the highly controlled environment of hospitals, where precision and safety are paramount, following HTM-02-01 guidelines for medical gas pipeline color coding is essential. It ensures the safe, efficient, and compliant delivery of gases that are critical for patient care. By adhering to these standards and regularly training staff, hospitals can significantly reduce the risk of gas-related incidents, ensuring a safer environment for both patients and healthcare providers.
Understanding and implementing proper medical gas pipeline color coding is not just a regulatory requirement—it’s a lifesaving measure. Make sure your facility complies with HTM-02-01 to promote the highest standards of safety in medical gas administration.







Leave a Reply