How to Use an Oxygen Cylinder Flow Meter for Accurate Gas Delivery
An oxygen cylinder flow meter is a crucial tool in healthcare, used to regulate and measure the flow of oxygen delivered to patients. For healthcare professionals and caregivers, ensuring the proper use of this device is vital for patient safety and effective treatment. This blog provides a comprehensive guide on how to use an oxygen cylinder flow meter correctly, as well as tips for ensuring accurate gas delivery.

What is an Oxygen Cylinder Flow Meter?
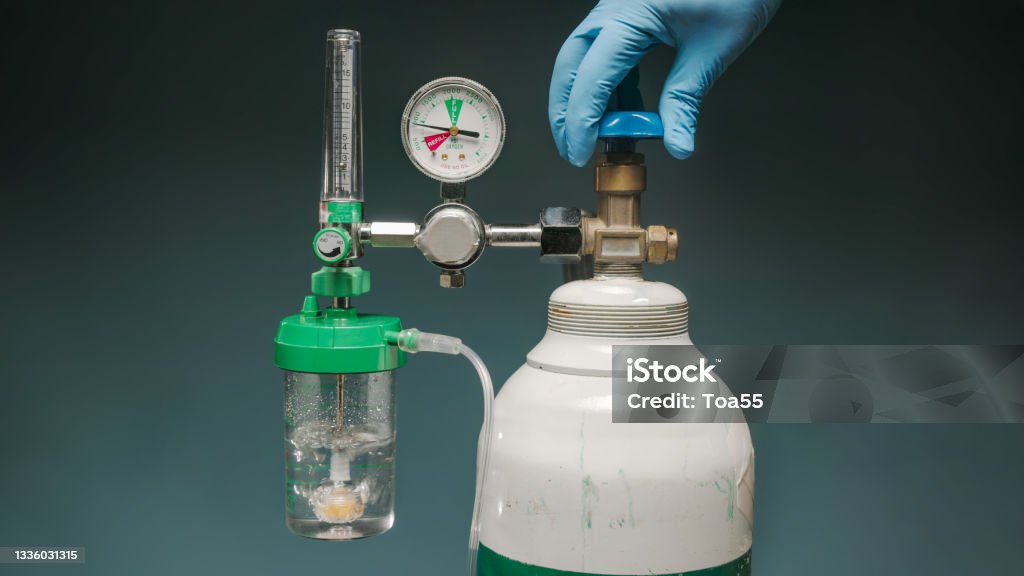
An oxygen cylinder flow meter is a device attached to the top of an oxygen cylinder. It controls the amount of oxygen the patient receives by adjusting the flow rate. The flow meter usually consists of:
- Pressure regulator: Regulates the pressure coming from the oxygen cylinder.
- Flow control knob: Allows you to adjust the flow of oxygen.
- Flow indicator (ball or gauge): Displays the flow rate in liters per minute (LPM), which is the rate at which oxygen is being delivered to the patient.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using an Oxygen Cylinder Flow Meter
Step 1: Setting Up the Oxygen Cylinder
Before connecting the flow meter, ensure that the oxygen cylinder is upright and secured in its stand. The cylinder must be in a stable position to avoid accidental tipping, which could damage the equipment.
Step 2: Attaching the Flow Meter
- Ensure the Cylinder is Off: Make sure the oxygen cylinder valve is closed.
- Secure the Flow Meter: Attach the flow meter securely to the cylinder’s regulator or outlet. This may require screwing the meter onto the cylinder valve until it is firmly attached.
- Check the Seal: Ensure that all connections are tightly secured to prevent leaks, which could lead to inaccurate oxygen flow or waste.
Step 3: Turning on the Oxygen Supply
- Open the Cylinder Valve: Slowly turn the valve on the oxygen cylinder counterclockwise to open the flow of oxygen. Listen for any hissing sounds indicating a leak.
- Adjust the Flow Control Knob: Turn the flow control knob on the flow meter to adjust the oxygen flow rate. Your healthcare provider should specify the exact flow rate required (typically measured in LPM).
Step 4: Reading the Flow Rate
- Observe the Flow Indicator: Depending on the type of flow meter, you will either have a ball floating inside a tube or a needle on a gauge. Adjust the flow control knob until the flow indicator aligns with the prescribed flow rate.
- Ensure Accuracy: Make sure to check the indicator from eye level for an accurate reading. The center of the ball should line up with the marked flow rate on the meter.
Step 5: Monitoring the Oxygen Delivery
- Check for Leaks: Ensure there are no leaks at the connection points. Leaks can cause a significant drop in oxygen delivery, leading to insufficient oxygen supply to the patient.
- Ensure Correct Flow: Periodically check that the flow meter is set to the correct rate and that it hasn’t been inadvertently changed.
Step 6: Shutting Off the Oxygen
- Turn Off the Cylinder: Once oxygen therapy is no longer needed, turn off the cylinder valve by rotating it clockwise.
- Release Excess Pressure: After the valve is closed, allow the remaining oxygen in the tube to flow out by leaving the flow control knob open. Once the flow indicator drops to zero, turn off the flow control knob.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
1. Incorrect Flow Rate Adjustment
Setting the wrong flow rate can result in the patient receiving too little or too much oxygen. Always double-check the prescribed rate.
2. Not Checking for Leaks
Leaks in the system can waste oxygen and reduce the amount of gas delivered to the patient. Use leak detection techniques (such as soapy water) to identify leaks at the connection points.
3. Improper Cylinder Positioning
Ensure the oxygen cylinder is always upright. If the cylinder falls over, the regulator and flow meter can become damaged, leading to inaccuracies in oxygen delivery.
4. Failure to Monitor Regularly
Even after setting the correct flow rate, it is important to continuously monitor the oxygen delivery, especially in long-term or critical care settings. Fluctuations in the flow rate can happen due to changes in the cylinder’s pressure.
Troubleshooting Tips
- Flow Rate Fluctuations: If the flow rate appears to fluctuate, check for leaks or damage to the flow meter. Also, ensure that the oxygen cylinder has sufficient gas pressure.
- Pressure Issues: If there is no oxygen flowing despite the valve being open, there may be an issue with the regulator or a blockage in the tubing.
- Alarm Systems: Some oxygen delivery systems are equipped with alarms that alert you if the flow rate falls below a certain threshold. Make sure you understand how these alarms function and what steps to take if an alarm sounds.
Why Accurate Gas Delivery Matters
The accuracy of oxygen delivery is crucial for patient safety and the effectiveness of the treatment. Inadequate oxygen can lead to hypoxia, while too much oxygen may cause oxygen toxicity. Proper use of an oxygen cylinder flow meter ensures that patients receive the precise amount of oxygen they need.
Maintenance and Care
- Regular Cleaning: To maintain the accuracy of the flow meter, clean it regularly as per the manufacturer’s instructions. Dust and debris can interfere with the flow indicator, leading to inaccurate readings.
- Routine Calibration: Over time, flow meters may lose calibration, which can affect the accuracy of oxygen delivery. Have the flow meter regularly serviced to ensure it is functioning correctly.
- Store Properly: When not in use, ensure the oxygen cylinder and flow meter are stored in a clean, dry area away from direct sunlight or extreme temperatures.
Conclusion
Using an oxygen cylinder flow meter correctly is essential for the accurate delivery of oxygen therapy. Following the steps outlined above will help ensure that patients receive the correct amount of oxygen to meet their medical needs. Proper use, combined with routine maintenance and troubleshooting, can prevent issues and ensure that the flow meter provides reliable and precise oxygen delivery in all settings, whether in a hospital or home care.







Leave a Reply