How Nebulization Works: A Step-by-Step Guide for Effective Respiratory Care
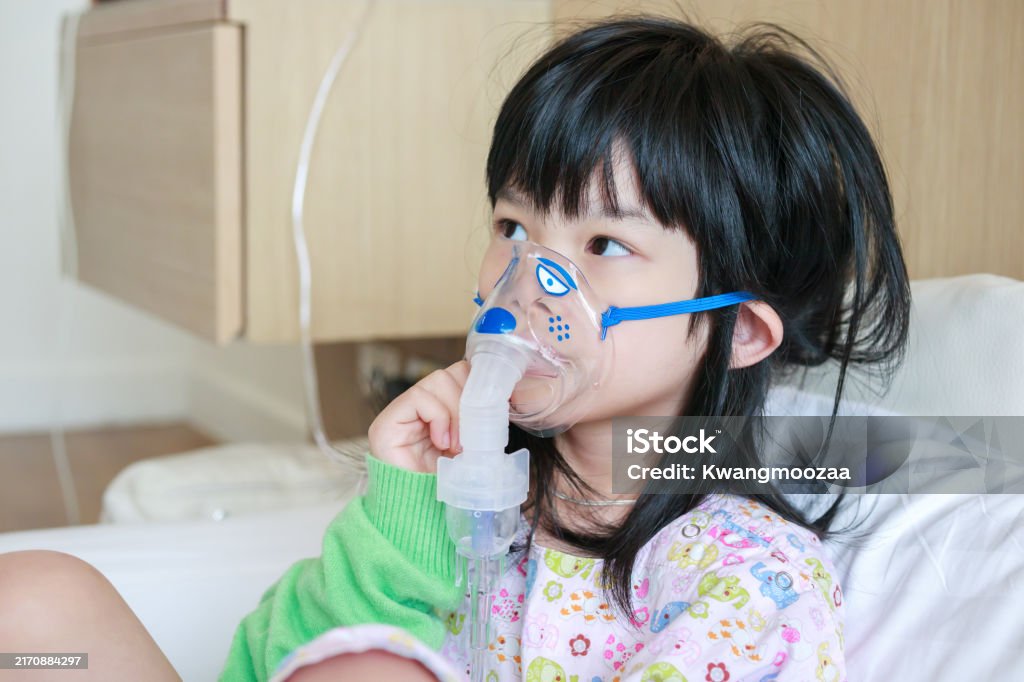
Nebulization is a common and effective method of delivering medication directly to the lungs, primarily used for managing respiratory conditions like asthma, COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease), and other lung infections. By transforming liquid medicine into a fine mist, nebulizers make it easier for patients to inhale medications and provide quicker relief.
In this blog, we’ll explore how nebulization works, its benefits, and how to use it properly for effective respiratory care.
What is Nebulization?
Nebulization involves converting liquid medications into a mist that can be inhaled into the lungs. The fine mist allows medication to be absorbed directly through the airways, providing faster relief, especially in emergency situations like asthma attacks or acute bronchitis flare-ups. Nebulizers are particularly useful for people who have difficulty using inhalers or need higher doses of medication.
Step-by-Step Process of Nebulization
- Preparation:
Before beginning the treatment, ensure the nebulizer machine is clean and in proper working order. Select the appropriate medication as prescribed by the healthcare provider. Typically, this comes in liquid vials pre-measured for each dose. - Setting Up the Nebulizer:
- Assemble the Device: Attach the compressor to the nebulizer cup, where the medication will be placed. Nebulizers usually consist of the main compressor, a mask or mouthpiece, a nebulizer cup for the medication, and tubing.
- Add Medication: Pour the prescribed liquid medication into the nebulizer cup. Some medications may be pre-mixed, while others may require the addition of saline.
- Connect Tubing: Attach the tube between the nebulizer cup and the air compressor.
- Positioning the Patient:
Whether the patient is using a mask or a mouthpiece, it’s crucial they sit upright during the treatment to allow proper inhalation of the medication. If using a mask, secure it comfortably over the nose and mouth. If using a mouthpiece, the patient should place it between their teeth and close their lips around it. - Starting the Treatment:
Turn on the nebulizer machine. The compressor forces air through the tube, turning the liquid medication into a mist that can be easily inhaled through the mouth or nose.- Breathing Technique: Inhale the mist slowly and deeply, holding the breath for a few seconds after each inhalation to allow the medication to settle in the lungs. The patient should continue to inhale deeply and steadily until all the medication has been administered.
- Monitoring the Process:
A typical nebulization session lasts between 10-15 minutes. It’s essential to monitor the mist flow—when the mist stops, it indicates the medication has been fully delivered. If there’s no mist, check the machine for blockages or leaks. - Post-Treatment Cleaning:
After each use, it’s crucial to clean the nebulizer parts to prevent contamination or infection. Disassemble the device and wash the nebulizer cup and mask or mouthpiece in warm, soapy water. Let them air dry before the next use. Regular deep cleaning is also recommended.
When is Nebulization Used?
Nebulization is particularly helpful in cases where patients:
- Cannot use inhalers correctly, such as young children, elderly individuals, or those with disabilities.
- Require higher doses of medication that inhalers cannot provide.
- Are experiencing acute exacerbations of chronic respiratory diseases.
Key Benefits of Nebulization
- Effective Medication Delivery: Nebulizers are extremely effective in delivering medication directly to the lungs, making them particularly useful for people with severe respiratory conditions.
- Easy to Use: Nebulizers are easier for patients who cannot use inhalers properly, such as the elderly or young children. They allow the patient to breathe normally while receiving the medication.
- Relief for Chronic Respiratory Conditions: Nebulization is commonly used in chronic conditions like asthma and COPD, where the patient needs ongoing respiratory treatment. It’s also used to manage acute respiratory infections.
- Customizable Treatment: Nebulizers can deliver a range of medications, including bronchodilators, corticosteroids, and antibiotics, depending on the patient’s needs.
Types of Nebulizers
There are various types of nebulizers available, each with its advantages:
- Jet Nebulizers:
The most common type, these use compressed air to turn liquid medication into a mist. They are reliable but tend to be bulky. - Ultrasonic Nebulizers:
These devices use high-frequency vibrations to create the mist. They are quieter than jet nebulizers and often more portable. - Mesh Nebulizers:
The most advanced type, mesh nebulizers use a mesh membrane to produce the mist. They are compact, efficient, and suitable for home and travel use.
Common Medications Used in Nebulization
- Bronchodilators (e.g., albuterol, levalbuterol): These help open up the airways, making breathing easier during asthma attacks or COPD exacerbations.
- Corticosteroids (e.g., budesonide): Reduce inflammation in the lungs, commonly prescribed for long-term asthma management.
- Antibiotics: Used in cases of respiratory infections, especially for conditions like cystic fibrosis.
- Mucolytics: These help to break down thick mucus in the lungs, making it easier to cough out.
Conclusion
Nebulization is an essential tool in respiratory care, offering effective, fast-acting treatment for conditions such as asthma, COPD, and bronchitis. Its ease of use, combined with the ability to deliver medications directly to the lungs, makes it a critical part of many patients’ daily care. Understanding how nebulization works and following best practices ensures that patients can breathe easier and manage their respiratory conditions more effectively.
If you or someone you care for uses a nebulizer, proper cleaning, maintenance, and adherence to medical advice are key to getting the most out of this treatment method. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice on nebulizer use and management.






Leave a Reply