The Importance of CSSD in Hospital Infection Control: A Detailed Workflow Overview
Infection control is a cornerstone of healthcare, particularly in hospitals, where patients are vulnerable to hospital-acquired infections (HAIs). One of the essential departments dedicated to ensuring sterility and patient safety is the Central Sterile Supply Department (CSSD). CSSD plays a pivotal role in hospital infection control by maintaining a sterile environment for medical instruments, surgical tools, and other reusable equipment. This blog explores the detailed workflow of the CSSD and highlights its importance in infection prevention.
What is CSSD?
The Central Sterile Supply Department (CSSD) is a specialized unit in hospitals responsible for cleaning, sterilizing, storing, and distributing surgical instruments and medical supplies. It ensures that all instruments are sterile and free from microbial contamination, a key factor in preventing infections during medical procedures.
CSSD’s Role in Infection Control
CSSD is critical in controlling the spread of infections within hospitals. It ensures that:
- Surgical instruments are sterile before and after procedures, minimizing the risk of introducing infections to patients.
- Medical supplies used in invasive procedures are decontaminated, cleaned, and sterilized according to hospital protocols.
- Effective sterilization methods are employed, reducing the possibility of HAIs.
Without a well-functioning CSSD, the risk of infection during surgical and diagnostic procedures increases significantly. Proper sterilization eliminates the transmission of bacteria, viruses, and fungi, ensuring patient safety.
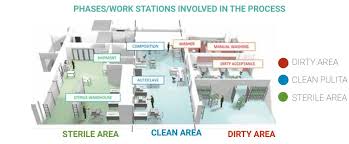
The CSSD Workflow: Step-by-Step
The CSSD follows a specific workflow to ensure that every instrument is processed correctly. Here’s a breakdown of the detailed steps involved in the workflow:
1. Decontamination
The first and most crucial step in the CSSD workflow is decontamination. After use, all medical instruments and tools are transported to the CSSD. The department typically uses a dedicated transportation route to avoid cross-contamination. In the decontamination area, the instruments are:
- Manually cleaned to remove visible debris and organic matter.
- Cleaned using ultrasonic cleaning machines or washer-disinfectors, which further remove any contaminants.
The decontamination step ensures that instruments are thoroughly cleaned before sterilization.
2. Inspection and Assembly
Once decontaminated, the instruments are carefully inspected for damage or residual contamination. A well-trained team ensures:
- Instruments are inspected for cracks, wear, or malfunction.
- Proper assembly of complex surgical instruments before sterilization.
Proper inspection and assembly are vital to ensure that instruments function correctly during surgeries.
3. Packaging and Preparation for Sterilization
After the inspection, instruments are packaged in sterile wraps or trays. Proper packaging is essential to maintain sterility post-sterilization. Depending on the type of instruments, different packaging materials may be used. During this phase:
- The instruments are arranged systematically for easy identification.
- Appropriate packaging is done to allow effective penetration of the sterilizing agent.
4. Sterilization
Sterilization is the heart of the CSSD workflow. Various sterilization methods are used, depending on the type of instruments and materials. The primary sterilization methods include:
- Steam Sterilization (Autoclaving): The most common and effective method, using high-pressure steam.
- Ethylene Oxide Gas (ETO): Used for heat-sensitive instruments.
- Hydrogen Peroxide Plasma: A low-temperature method for delicate instruments.
- Dry Heat Sterilization: Suitable for instruments that can tolerate high temperatures.
The sterilization process eliminates all forms of microbial life, including bacteria, spores, and viruses, ensuring that the instruments are entirely safe for patient use.
5. Storage and Distribution
Once sterilized, the instruments are stored in sterile conditions within the CSSD until they are required for medical procedures. The storage area must be:
- Clean, sterile, and well-organized, with designated areas for different instruments.
- Regularly monitored to ensure proper environmental conditions (temperature, humidity) that maintain sterility.
The CSSD is also responsible for distributing sterilized instruments to various departments, including operating theaters and outpatient clinics.
Importance of Staff Training and Compliance
A key element of CSSD effectiveness is well-trained staff. CSSD personnel must be familiar with sterilization techniques, hospital infection control protocols, and the safe handling of medical instruments. Regular training and updates on the latest sterilization technologies help ensure compliance with healthcare standards.
Moreover, infection control teams work closely with CSSD staff to ensure that all procedures align with national and international infection prevention standards, such as those outlined by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Conclusion: CSSD – A Vital Role in Infection Prevention
The CSSD plays a fundamental role in infection control within hospitals. By adhering to stringent sterilization protocols and ensuring that all medical instruments are free from contamination, CSSD helps reduce the risk of hospital-acquired infections. The well-structured workflow from decontamination to sterilization and storage ensures that surgical and diagnostic procedures are conducted in a sterile environment, promoting patient safety and better health outcomes.
Hospitals must continue to invest in the latest sterilization technologies, staff training, and infection control protocols to ensure the efficiency of their CSSD departments. Ultimately, a robust CSSD is not just a support service; it is a vital department in the fight against infections and the promotion of safe, sterile healthcare environments.





Leave a Reply