Electrocautery vs. Harmonic Scalpel: A Comprehensive Guide for Surgeons
Modern surgical tools have revolutionized the precision and safety of procedures, allowing surgeons to minimize complications and promote faster healing. Two of the most commonly used tools in contemporary surgeries are electrocautery and the harmonic scalpel. Each has unique characteristics, advantages, and limitations that are important for surgeons to understand. In this blog, we will dive into the key differences between these two technologies, helping you make informed decisions for your surgical practice.
1. Understanding the Basics: What Are Electrocautery and Harmonic Scalpel?
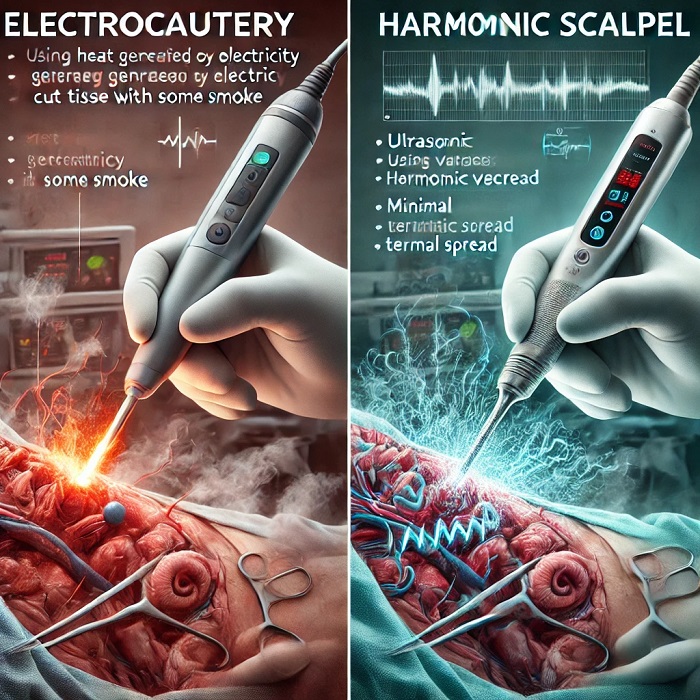
Electrocautery is a surgical tool that uses electrical current to generate heat, which is then applied to tissue for cutting or coagulation. The heat generated can cut tissue or stop bleeding by coagulating blood vessels, making it an essential tool in surgeries where blood loss control is critical.
Harmonic Scalpel, on the other hand, uses ultrasonic vibrations to cut and coagulate tissues. This device operates at high frequencies (around 55.5 kHz), using mechanical energy instead of electrical heat to achieve both cutting and coagulation with minimal thermal spread.
2. Mechanism of Action
Electrocautery relies on the conduction of an electric current through a resistant wire, which heats up and causes localized tissue damage through burning. The tissue destruction and sealing of blood vessels help control bleeding. However, this can also cause significant heat transfer to surrounding tissues, increasing the risk of thermal injury.
Harmonic Scalpel, in contrast, uses ultrasonic energy that causes the tissues to vibrate rapidly. This mechanical vibration disrupts the protein structure of the tissues, cutting them and simultaneously sealing blood vessels through protein denaturation. The heat generated is significantly less than electrocautery, reducing thermal damage to adjacent tissues.
3. Applications in Surgery
Electrocautery is versatile and is used in a wide range of surgeries, including open and laparoscopic procedures. It’s often the tool of choice for surgeries where precise bleeding control is necessary, such as in vascular, plastic, and orthopedic surgeries.
The harmonic scalpel is frequently used in minimally invasive surgeries, such as laparoscopic procedures, ENT surgeries, and gynecological surgeries. It is especially useful in delicate procedures where minimizing heat damage to surrounding tissues is crucial, such as in thyroidectomy and bowel resection.
4. Thermal Damage and Tissue Healing
One of the biggest differentiators between the two tools is the amount of thermal damage they cause. Electrocautery can cause significant heat build-up in surrounding tissues, which may lead to more extensive tissue damage, increased healing times, and a higher risk of complications such as tissue necrosis.
On the other hand, the harmonic scalpel operates at a much lower temperature, which minimizes the risk of thermal injury. This makes it ideal for delicate surgeries where precision is required, and faster healing is a priority.
5. Bleeding Control and Coagulation Efficiency
Electrocautery is known for its excellent coagulation capabilities. By burning tissue and blood vessels, it can effectively stop bleeding during surgeries, making it a highly reliable tool for bleeding control.
The harmonic scalpel, while also capable of cutting and coagulating, works through protein denaturation rather than burning. While this provides better control in specific scenarios, especially in delicate surgeries, the coagulation effect may not be as strong as electrocautery for managing larger blood vessels.
6. Smoke Production and Surgical Visibility
One downside of electrocautery is that it produces more smoke during operations, which can hinder the surgeon’s view. Surgical smoke contains potentially harmful chemicals and particles, which may affect both patients and operating room staff.
In contrast, the harmonic scalpel produces minimal smoke due to its lower operating temperature. This contributes to better visibility during procedures and a cleaner operating environment.
7. Cost Considerations
The initial cost of a harmonic scalpel system is higher than that of an electrocautery unit. The disposable blades of the harmonic scalpel are also more expensive compared to the relatively lower cost of electrocautery tips. However, the harmonic scalpel’s potential to reduce complications, speed up recovery, and lower the risk of tissue damage may offset these initial expenses in specific surgeries.
8. Which Tool Should You Choose?
When deciding between electrocautery and a harmonic scalpel, consider the following factors:
- Type of Surgery: For general surgeries requiring rapid, broad tissue cutting with coagulation, electrocautery may be the better choice. For delicate surgeries where precision and minimal thermal damage are essential, the harmonic scalpel could be more advantageous.
- Bleeding Control: If bleeding is a major concern, electrocautery offers stronger coagulation. However, in procedures where you want to minimize tissue damage, harmonic scalpel’s gentle action is preferable.
- Surgical Setting: For minimally invasive surgeries, especially laparoscopic and endoscopic procedures, the harmonic scalpel provides more control with less thermal spread and less smoke.
- Cost and Availability: Budget and access to the instruments may also play a role in determining which tool to use. Harmonic scalpels are generally more expensive but can reduce overall complications and recovery time, improving long-term cost-effectiveness in some settings.
Conclusion
Both electrocautery and the harmonic scalpel are vital tools in modern surgery, offering different benefits based on the type of procedure. Electrocautery remains a go-to tool for bleeding control and rapid tissue cutting, while the harmonic scalpel is ideal for delicate, minimally invasive surgeries. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each tool will help surgeons choose the most appropriate instrument for each procedure, enhancing patient safety and improving surgical outcomes.






Leave a Reply