Understanding How an Anesthesia Machine Works: A Comprehensive Guide for Healthcare Professionals
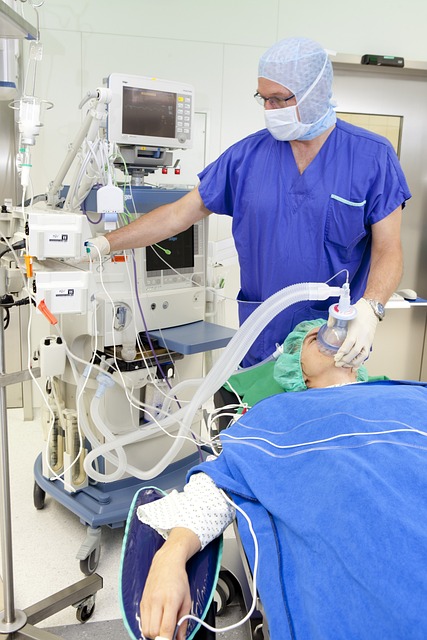
Anesthesia machines are essential in modern medical practice, ensuring patients are safely and effectively sedated during surgeries and other medical procedures. They provide a continuous supply of medical gases, mixed with an anesthetic agent, and ensure patients remain unconscious and pain-free during surgery. In this blog, we’ll explore the core components, functionality, and importance of anesthesia machine in healthcare settings.
Key Components of an Anesthesia Machine
An anesthesia machine has several critical components, each playing a specific role in delivering safe anesthesia. Here are the main parts:
- Gas Delivery System
The gas delivery system is the heart of the anesthesia machine. It regulates the flow of essential medical gases, such as Oxygen, Nitrous oxide, and air, from their storage cylinders or pipelines into the machine. The flow of these gases is measured by flow-meters, and they are mixed to create the right concentration before entering the patient’s breathing system. - Vaporizers
The vaporizers are used to convert liquid anesthetic agents (such as isoflurane, sevoflurane, or desflurane) into a gas form. These gases are then added to the oxygen or air that is delivered to the patient. Vaporizers allow for precise control over the concentration of anesthetic agents, ensuring proper sedation without overdose. - Breathing Circuit
The breathing circuit is the system that delivers the anesthetic gases from the machine to the patient’s lungs. It consists of tubing, valves, and a reservoir bag. Modern circuits have unidirectional valves to prevent exhaled gases from being rebreathed unless they pass through a carbon dioxide absorber (like soda lime). - Ventilator
In cases where patients are unable to breathe on their own, the anesthesia machine’s ventilator steps in. The ventilator controls the flow of gases into the patient’s lungs, maintaining adequate oxygen levels and removing carbon dioxide. It allows for precise control over the rate, volume, and pressure of breaths delivered. - Monitoring Systems
Advanced anesthesia machines are equipped with integrated monitoring systems. These monitors track vital parameters such as oxygen levels, carbon dioxide levels, heart rate, and blood pressure. Continuous monitoring allows healthcare providers to respond quickly if any issues arise during surgery. - Scavenging System
The scavenging system ensures that any excess anesthetic gases exhaled by the patient or leaked into the environment are safely removed from the operating room. This system is critical for protecting healthcare workers from exposure to potentially harmful gases.
How the Machine Works Step by Step
- Gas Flow Control
The machine begins by regulating the flow of oxygen, air, and other medical gases. These gases are mixed to the required proportions using flow-meters, ensuring that the patient receives the correct levels of oxygen and anesthetic. - Vaporizer Function
The mixed gases pass through the vaporizer, which adds the appropriate anesthetic agent. Vaporizers precisely control the amount of anesthetic in the gas mixture to maintain the desired level of sedation. - Delivery to the Patient
The gas mixture is delivered to the patient through the breathing circuit, either through a mask or a breathing tube (endotracheal tube). If the patient cannot breathe independently, the ventilator assists in maintaining a consistent oxygen supply. - Monitoring and Adjustments
Throughout the procedure, the machine monitors the patient’s vital signs, allowing the anesthesiologist to make necessary adjustments to the oxygen or anesthetic levels. The system ensures the patient remains unconscious while preventing complications like hypoxia or excessive sedation. - Exhaled Gas Management
Exhaled gases are passed through a carbon dioxide absorber, which removes carbon dioxide, allowing for safe rebreathing of the remaining gases. Any excess gases are safely removed from the operating room via the scavenging system.
Importance of Anesthesia Machines in Healthcare
Anesthesia machines are designed to ensure patient safety by maintaining optimal levels of oxygen and anesthetic gases throughout the surgery. The precise control they offer in managing gas delivery and ventilation allows for effective sedation, minimizes the risk of complications, and ensures rapid patient recovery post-operation. These machines are essential not only for the surgical team but also for the well-being of the patient.
Conclusion
Understanding how anesthesia machines work is essential for healthcare professionals working in surgical environments. From the gas delivery system to the monitors and safety features, each component plays a crucial role in ensuring patient safety during anesthesia. As medical technology advances, so too will the capabilities of these life-saving machines, making them an indispensable part of modern healthcare.






Leave a Reply