Types of Patient Monitoring Equipment: Ensuring Safety in Every Hospital Ward
In today’s healthcare, patient monitoring equipment is key for keeping patients safe. These devices track vital signs in real-time. This lets doctors quickly respond to any changes in a patient’s health.
These systems not only help patients get better but also give valuable data. This data helps doctors make better diagnoses and treatments. Here are some common types of patient monitoring equipment found in hospitals.
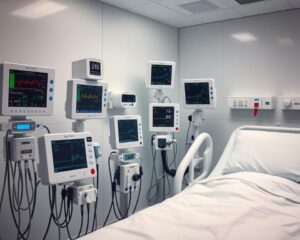
1. Electrocardiogram (ECG) Monitors
ECG monitors track the heart’s electrical activity. They are non-invasive and help spot heart issues like arrhythmias and heart attacks.
How it works:
Electrodes on the skin record the heart’s electrical impulses. These are shown in real-time, giving doctors a clear view of the heart’s function.
Common uses:
ECG monitors are used in emergency rooms, ICUs, and general wards. They are especially useful for patients with chest pain or irregular heartbeats.
2. Pulse Oximeters
Pulse oximeters measure oxygen levels in the blood. They are small, non-invasive, and often clipped to a finger or earlobe.
How it works:
They use light absorption to measure oxygen in red blood cells. The device shows oxygen saturation and pulse rate.
Common uses:
They are crucial for patients with respiratory issues like COPD and COVID-19. They are also used for patients recovering from surgery.
3. Blood Pressure Monitors
Blood pressure monitoring is vital in patient care. Automatic blood pressure monitors measure systolic and diastolic pressure. They provide a quick, non-invasive way to check cardiovascular health.
How it works:
The monitor inflates a cuff around the arm. It then releases pressure to measure blood flow through arteries.
Common uses:
BP monitors are used in every ward. They are especially important for patients at risk of high or low blood pressure.
4. Capnography Monitors
Capnography monitors measure CO2 in exhaled breath. They assess respiratory function. These monitors are used for patients under anesthesia or needing mechanical ventilation.
How it works:
They measure CO2 in exhaled air. This helps doctors check breathing and oxygen delivery.
Common uses:
Capnography monitors are key in operating rooms, post-anesthesia units, and ICUs. They are used for intubated or sedated patients.
5. Temperature Monitors
Temperature monitors track body temperature, especially in infections or inflammation. They help detect fevers early and guide treatment.
How it works:
Electronic thermometers are placed on or inside the body. They provide continuous or periodic readings. Some systems work with other vital sign monitors for comprehensive care.
Common uses:
Temperature monitors are used in all wards. They are especially important for patients with infections, post-operative patients, and in neonatal care.
6. Fetal Monitors
Fetal monitors track the heart rate and other vital signs of a fetus. They are used during pregnancy and labor. This ensures the safety of both mother and baby during delivery.
How it works:
External or internal sensors track the baby’s heart rate and the mother’s contractions. They display the data for doctors and nurses to interpret in real-time.
Common uses:
Fetal monitors are standard in labor and delivery units. They are especially used during high-risk pregnancies and complicated labor.
7. Glucose Monitors
Blood glucose monitors measure the level of glucose in a patient’s blood. This is crucial for managing conditions like diabetes. These monitors are particularly useful in intensive care units.
How it works:
A small sample of blood is taken and analyzed by the monitor. It determines the glucose concentration.
Common uses:
Glucose monitors are essential for patients with diabetes. They are used throughout hospitals, especially in intensive care, where blood sugar levels must be tightly controlled.
8. Central Monitoring Systems
Central monitoring systems allow healthcare providers to monitor multiple patients at once. They integrate data from various bedside monitors, such as ECG, pulse oximeters, and blood pressure monitors.
How it works:
Data from individual monitors is transmitted to a central hub. Healthcare staff can observe multiple patients’ vital signs on one screen.
Common uses:
Central monitoring systems are essential in ICUs, neonatal units, and emergency departments. Patients require constant surveillance.
9. Infusion Pumps with Monitoring Capabilities
Infusion pumps are used to administer medications, fluids, and nutrients to patients. Smart infusion pumps with integrated monitoring systems ensure the right dosage is delivered at the correct rate. This reduces the risk of human error.
How it works:
The pump regulates the flow of medication or fluids into the patient’s bloodstream. It monitors the rate and volume administered.
Common uses:
These are crucial in intensive care, oncology units, and post-operative care. They deliver medications like insulin, chemotherapy, or anesthesia.
10. Telemetry Monitors
Telemetry systems allow for the remote monitoring of patients’ vital signs. This enables continuous observation without needing the patient to be confined to a hospital bed. It is useful for ambulatory patients or those who need to move around while still being monitored.
How it works:
Wireless sensors transmit data to a remote central monitor. Healthcare providers can track heart rate, respiratory rate, and oxygen levels.
Common uses:
Telemetry is commonly used in cardiac care units, post-surgical recovery, and for patients transitioning from ICU to general wards.
Conclusion
Patient monitoring equipment is essential for maintaining safety across every hospital ward. These devices provide real-time data on a patient’s vital signs. This enables healthcare professionals to detect issues early and respond promptly.
From the ICU to general wards, reliable monitoring systems improve patient outcomes. They also streamline hospital operations. This allows for more effective, data-driven care.






Food
My brother suggested I might like this website. He was entirely right. This post actually made my day. You cann’t imagine simply how much time I had spent for this information! Thanks!