Modular vs. Conventional OTs: Enhancing Surgical Precision and Hospital Efficiency
Operating theatres (OTs) are the heart of any hospital, providing critical spaces for surgeries and life-saving interventions. As technology advances, hospitals are increasingly considering upgrading to modular OTs or sticking with conventional OTs. While both types are essential to enabling surgical procedures, modular OTs have emerged as a superior option due to their enhanced features, sterility, and efficiency. This blog explores the key differences between modular and conventional OTs and how modular setups transform modern surgery’s landscape.
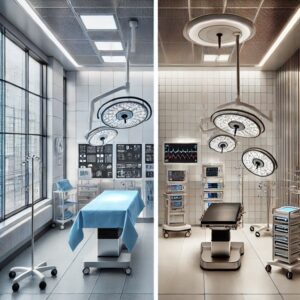
1. Design and Construction
- Modular OT:
Modular OTs are prefabricated and assembled using high-quality, standardized materials such as steel panels, anti-bacterial wall surfaces, and ceilings. These OTs are typically designed off-site and then quickly installed within the hospital, allowing for faster construction and less disruption to hospital operations. They are customizable, making them adaptable to any hospital’s unique surgical requirements - Conventional OT:
Traditional or conventional OTs are constructed on-site using a variety of materials and systems, often requiring coordination between multiple vendors. This lack of standardization can increase costs and lead to delays. Additionally, these OTs may not have the same level of flexibility for upgrades or expansions
2. Sterility and Infection Control
- Modular OTs:
A major advantage of modular OT is their superior infection control features. They often come equipped with laminar air flow systems that deliver sterile, bacteria-free air to the operating area. Additionally, modular OT use anti-bacterial wall and ceiling materials, helping reduce the risk of infection during surgeries. These features ensure a controlled, sterile environment, which is critical in reducing postoperative infections - Conventional OTs:
While conventional OT can maintain cleanliness, they often lack the advanced air filtration and sterilization systems found in modular OT. The materials used in their construction may also not provide the same level of resistance to bacterial growth, making them more challenging to maintain at optimal levels of sterility
3. Technology Integration
- Modular OT:
Modular OTs are designed with cutting-edge technology, allowing seamless integration of electronic control panels, data management systems, and surgical recording systems. Surgeons can monitor air quality, adjust temperature and humidity, and even control lighting directly from an integrated panel. Moreover, real-time surgical recording and data management systems help improve surgical outcomes and support teaching and training - Conventional OTs:
Conventional OTs often rely on external systems for monitoring and control, which can result in inefficiencies. They may not be as integrated or centralized as modular OTs, potentially leading to delays in accessing critical data during surgery
4. Maintenance and Durability
- Modular OT:
The prefabricated nature of modular OT makes maintenance easier and less invasive. With features such as hermetically sealed doors and wall panels that resist wear, modular OTs are designed for longevity. Maintenance tasks, such as air filter replacements or electrical repairs, can be done quickly with minimal disruption to the surgical schedule - Conventional OT:
Conventional OTs are built with a variety of materials, often leading to inconsistent durability. As a result, they may require more frequent repairs or updates, which can disrupt hospital operations and add to long-term costs
5. Cost and Installation Time
- Modular OTs:
Although modular OTs may have a higher upfront cost, they offer long-term savings due to their durability, efficiency, and lower maintenance requirements. Their quick installation time is another key advantage, with modular OTs often being installed in weeks, compared to months for conventional OTs - Conventional OTs:
Conventional OTs, while potentially less expensive initially, often take longer to build and may incur higher long-term costs due to frequent repairs, updates, and less efficient workflows
6. Customization and Flexibility
- Modular OTs:
One of the standout features of modular OT is their flexibility. Hospitals can customize the design, equipment, and layout to meet specific needs. As surgical techniques and equipment evolve, modular OTs can be upgraded or reconfigured more easily, allowing hospitals to stay current with the latest medical advancements - Conventional OTs:
Conventional OTs are typically more rigid in design. Once constructed, making modifications or upgrades can be time-consuming and costly. This lack of flexibility may limit the hospital’s ability to adopt new technologies or improve surgical efficiency
Conclusion
The debate between modular and conventional OTs ultimately comes down to a hospital’s needs for flexibility, efficiency, and long-term value. Modular OTs offer a technologically advanced, sterile, and highly efficient environment that not only improves surgical precision but also reduces the risk of infection and enhances hospital efficiency. Conventional OTs, while functional, may not provide the same level of performance or adaptability to future advancements. As hospitals continue to evolve, the modular OT represents the future of surgical care, ensuring that patient outcomes and operational efficiency remain at the forefront.






Leave a Reply